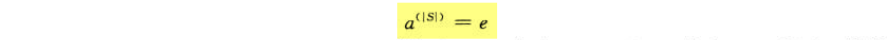31.1 基础数论概念
整除性与约数
素数与合数
除法定理、余数和等模
公约数与最大公约数
互质数
唯一因子分解定理
31.2 最大公约数
欧几里得算法
递归调用次数
int euclid(int a, int b){
if(b == 0){
return a;
}else{
return euclid(b, a%b);
}
}
欧几里得算法的扩展形式
- 用于计算满足下列条件的整系数
- 递归调用次数
// 法1
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int d, x, y;
void extendedEuclid(int a, int b){
if(b == 0){
d = a, x = 1, y = 0;
}else{
extendedEuclid(b, a%b);
int tempX = x;
x = y, y = tempX-(int)floor(a/b)*y;
}
}
int main() {
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
extendedEuclid(a, b);
printf("%d = gcd(%d, %d) = %d*%d+%d*%d", d, a, b, a, x, b, y);
return 0;
}
// 法2
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int exgcd(int a, int b, int &x, int &y){
if(b == 0){
x = 1, y = 0;
return a;
}
int g = exgcd(b, a%b, y, x);
y -= a/b*x;
return g;
}
int main() {
int a, b, x, y;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
int d = exgcd(a, b, x, y);
printf("%d = gcd(%d, %d) = %d*%d+%d*%d", d, a, b, a, x, b, y);
return 0;
}
31.3 模运算
有限群
由模加法和模乘法所定义的群
子群
由一个元素生成的子群