1 线段的性质
1.1 一些定义
1.2 确定连续线段是向左转还是向右转
已知
计算
- 结果
- 结果
- 结果
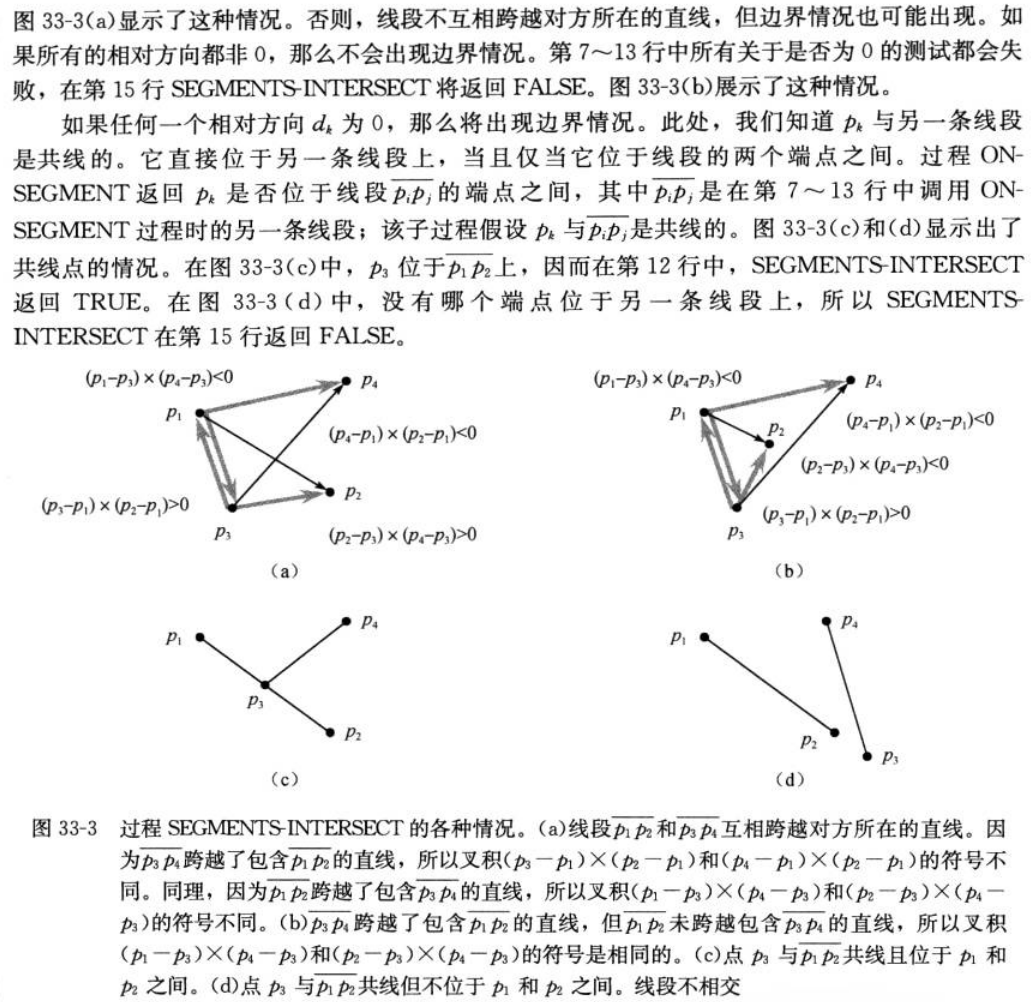
1.3 判定两条线是否相交
伪代码
cpp实现
struct dot{
int x, y;
};
int direction(dot pi, dot pj, dot pk){
return ((pk.x-pi.x)*(pj.y-pi.y)-(pk.y-pi.y)*(pj.x-pi.x));
}
bool onSegment(dot pi, dot pj, dot pk){
if(min(pi.x, pj.x) <= pk.x && max(pi.x, pj.x) >= pk.x &&
min(pi.y, pj.y) <= pk.y && max(pi.y, pj.y) >= pk.y){
return true;
}
return false;
}
/*
* 线段p1p2与p3p4是否相交
*/bool segmentsIntersect(dot p1, dot p2, dot p3, dot p4){
int d1 = direction(p3, p4, p1);
int d2 = direction(p3, p4, p2);
int d3 = direction(p1, p2, p3);
int d4 = direction(p1, p2, p4);
if(((d1>0 && d2<0)||(d1<0 && d2>0)) && ((d3>0 && d4<0)||(d3<0 && d4>0))){
return true;
}else if(d1 == 0 && onSegment(p3, p4, p1)){
return true;
}else if(d2 == 0 && onSegment(p3, p4, p2)){
return true;
}else if(d3 == 0 && onSegment(p1, p2, p3)){
return true;
}else if(d4 == 0 && onSegment(p1, p2, p4)){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
2 确定任意一对线段是否相交
O(nlgn)的红黑树(未实现)
- 简化
- 线段排序
- 移动扫除线
- 求线段交点的伪代码
简单易懂的O(n^2)的cpp实现
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct Point {
int x, y;
Point operator+(const Point &b) const {
return {x + b.x, y + b.y};
}
Point operator-(const Point &b) const {
return {x - b.x, y - b.y};
}
Point operator*(const int &b) const {
return {x * b, y * b};
}
int operator^(const Point &b) const {
return x * b.y - y * b.x;
}
};
struct Line {
Point p;
Point q;
};
vector<Line> lines;
int sgn(int x);
bool intersect(Line l1, Line l2);
bool onSegment(Point point, Line line);
int main() {
int n, cnt = 0;
cin >> n;
int x1, y1, x2, y2;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2;
lines.push_back({{x1, y1}, {x2, y2}});
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
if (intersect(lines[i], lines[j]))
cnt++;
cout << cnt;
return 0;
}
int sgn(int x) {
if (x < 0) return -1;
if (x > 0) return 1;
return 0;
}
bool intersect(Line l1, Line l2) {
int d1 = sgn((l1.q - l1.p) ^ (l2.p - l1.p));
int d2 = sgn((l1.q - l1.p) ^ (l2.q - l1.p));
int d3 = sgn((l2.q - l2.p) ^ (l1.p - l2.p));
int d4 = sgn((l2.q - l2.p) ^ (l1.q - l2.p));
if (d1 * d2 < 0 && d3 * d4 < 0)
return true;
if (d1 == 0 && onSegment(l2.p, l1))
return true;
if (d2 == 0 && onSegment(l2.q, l1))
return true;
if (d3 == 0 && onSegment(l1.p, l2))
return true;
if (d4 == 0 && onSegment(l1.q, l2))
return true;
return false;
}
bool onSegment(Point point, Line line) {
if (point.x >= min(line.p.x, line.q.x) &&
point.x <= max(line.p.x, line.q.x) &&
point.y >= min(line.p.y, line.q.y) &&
point.y <= max(line.p.y, line.q.y))
return true;
return false;
}
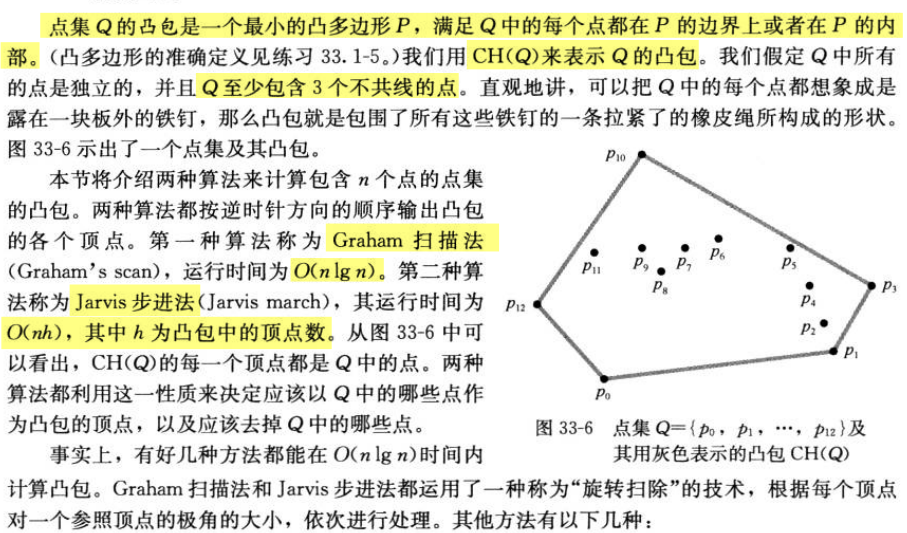
3 寻找凸包
Graham扫描法
Jarvis步进法
Graham扫描法 cpp实现
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 200005;
const double eps = 1e-7;
struct Point {
double x, y;
Point operator+(const Point &b) const {
return {x + b.x, y + b.y};
}
Point operator-(const Point &b) const {
return {x - b.x, y - b.y};
}
double operator^(const Point &b) const {
return x * b.y - y * b.x;
}
bool operator<(const Point &b) const {
if (x != b.x)
return x < b.x;
return y < b.y;
}
};
Point p[MAX];
Point s[MAX];
int top;
void selMin(int n);
int cmp(Point a, Point b);
bool equal(double a, double b);
double dis(Point a, Point b);
void graham(int n);
double s_sqr(Point a, Point b, Point c);
double diameter();
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> p[i].x >> p[i].y;
selMin(n);
sort(p + 1, p + n, cmp);
graham(n);
printf("%.6f", sqrt(diameter())) ;
return 0;
}
void selMin(int n) {
Point Min = p[0];
int IDMin = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (p[i] < Min) {
Min = p[i];
IDMin = i;
}
swap(p[0], p[IDMin]);
}
int cmp(Point a, Point b) {
double x = (a - p[0]) ^ (b - p[0]);
if (x > 0)
return 1;
if (equal(x, 0) && (dis(a, p[0]) < dis(b, p[0])))
return 1;
return 0;
}
double dis(Point a, Point b) {
double x = a.x - b.x;
double y = a.y - b.y;
return x * x + y * y;
}
void graham(int n) {
top = 1;
s[0] = p[0];
s[1] = p[1];
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
while (top > 1 && ((p[i] - s[top]) ^ (s[top - 1] - s[top])) <= 0)
top--;
s[++top] = p[i];
}
}
double s_sqr(Point a, Point b, Point c) {
return fabs((a - b) ^ (c - b));
}
double diameter() {
double diam = 0;
int j = 2;
s[++top] = s[0];
if (top < 3)
return dis(s[0], s[1]);
for (int i = 0; i < top - 1; i++) {
while (s_sqr(s[i], s[i + 1], s[j]) < s_sqr(s[i], s[i + 1], s[(j + 1) % top]))
j = (j + 1) % top;
diam = max(diam, max(dis(s[i], s[j]), dis(s[i + 1], s[j])));
}
return diam;
}
bool equal(double a, double b){
return fabs(a - b) < eps;
}
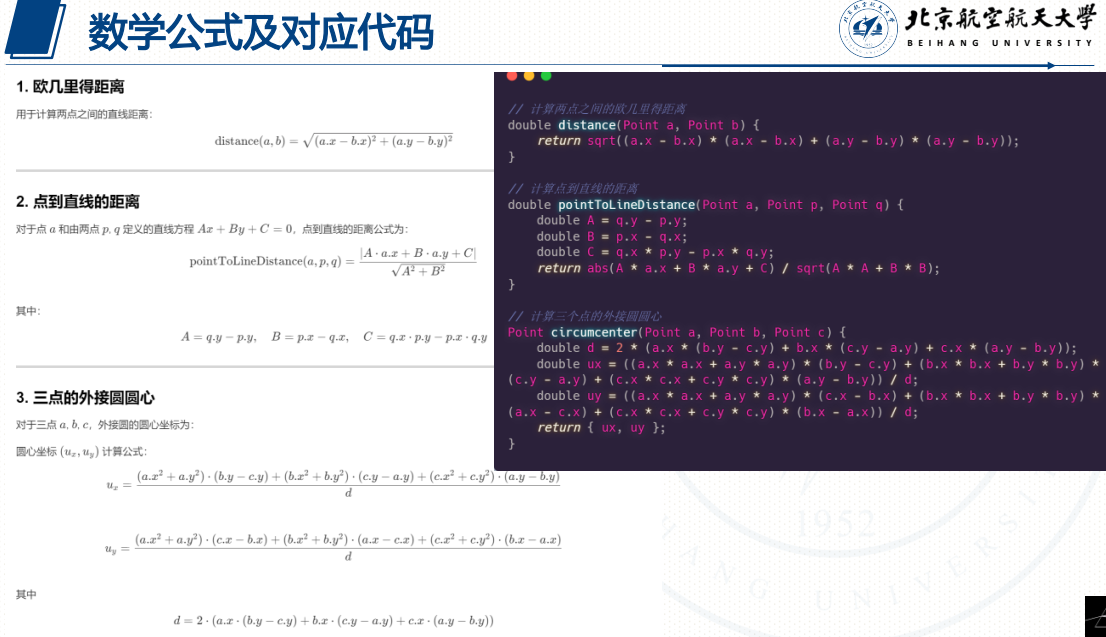
4 其他会用到的公式